Choosing the right heating system for your home can significantly affect your comfort, energy efficiency, and overall costs. Homeowners often weigh the pros and cons of HRV (Heat Recovery Ventilation) heating systems versus traditional HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. HRV Heating System offers a modern solution focusing on ventilation and energy recovery, making them suitable for improving air quality and reducing energy usage. On the other hand, traditional HVAC systems are widely recognised for managing heating and cooling needs effectively, making them versatile options for various climates. This blog aims to guide you through both systems’ key features and benefits to help you make an informed decision.
Comprehending HRV Systems
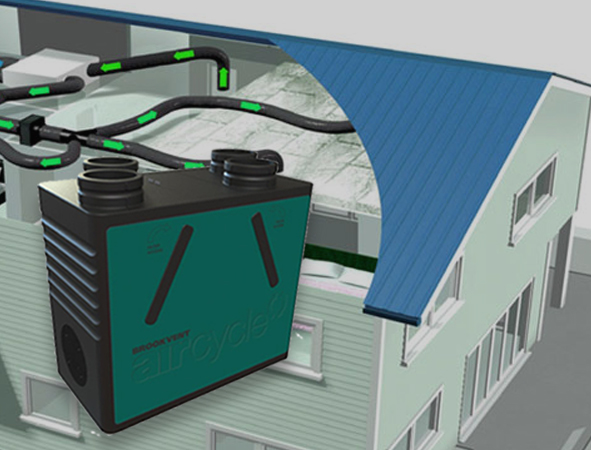
Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) systems are designed to optimise indoor air quality while enhancing energy efficiency. By extracting heat from the outgoing air and transferring it to incoming fresh air, HRV systems help maintain a comfortable indoor temperature without additional heating. This process efficiently recycles heat that would otherwise be lost, leading to significant reductions in heating costs. Over time, this energy-saving mechanism translates to lower utility bills and a more sustainable home environment.
Consistent Fresh Air Supply
HRV systems continuously provide fresh air to indoor spaces by replacing stale, contaminated air with clean, filtered outdoor air. This continuous exchange of air ensures a constant supply of fresh oxygen, helping to maintain a healthy living environment. Unlike traditional ventilation methods that may rely on windows or mechanical fans, HRVs offer a more consistent and controlled approach to air circulation, making them ideal for homes with limited natural ventilation or urban areas with higher pollution levels.
Improved Indoor Air Quality
One of the primary benefits of HRV systems is their ability to improve indoor air quality. By continuously removing stale air and replacing it with fresh air, HRVs help reduce indoor pollutants such as dust, allergens, and moisture buildup. This is particularly beneficial for people with respiratory conditions or allergies, ensuring their air is cleaner and healthier. The consistent air exchange also reduces the risk of condensation, mould, and mildew growth, contributing to a more comfortable and hygienic indoor environment.
Exploring Conventional HVAC Systems
Traditional HVAC systems work by heating or cooling air and distributing it throughout the home. These systems include furnaces, air conditioners, and ductwork to regulate indoor temperature. HVAC systems are generally well-suited for homes in diverse climates due to their capacity to provide both heating and cooling solutions. Their effectiveness in maintaining a stable indoor environment makes them a popular choice for many homeowners.
While they require periodic servicing, traditional HVAC systems are known for their reliability and ability to handle fluctuating weather conditions. Including advanced thermostats and zoning options in some models can further enhance their efficiency and performance.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
HRV systems are designed to recover and reuse typically lost heat, leading to lower overall energy consumption. This is achieved by transferring warmth from outgoing air to incoming fresh air, reducing the need for additional heating. As a result, homeowners can experience significant energy savings and lower utility bills over time. In contrast, traditional HVAC systems often consume more energy to maintain desired indoor temperatures, as they do not inherently recycle heat. Although some modern HVAC models incorporate energy-efficient features like advanced thermostats and zoning, they still need to catch up to HRV systems in overall energy efficiency.
Installation Factors
HRV systems often necessitate installation during new constructions or extensive renovations, requiring a dedicated duct network for adequate ventilation. The specialised equipment and setup can lead to higher initial installation costs. Conversely, traditional HVAC systems can be integrated into existing structures relatively quickly, although installation expenses can vary based on the complexity and type of system being retrofitted. Both systems require careful planning and professional installation to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Maintenance Demands
HRV systems require routine filters and heat exchanger cleaning to maintain optimal efficiency. This includes periodic checks to ensure the system is free from blockages and that airflow remains consistent. In comparison, traditional HVAC systems demand regular filters, coils, and ductwork servicing to ensure they function correctly. Both systems benefit from professional inspections to identify and address potential issues early on.
Regular maintenance tasks differ slightly, with HRV systems focusing more on the ventilation components, while HVAC systems may require more extensive upkeep due to their multifaceted nature. Ignoring maintenance can lead to reduced efficiency and increased energy costs for both systems.
Climate Compatibility with HRV Ventilation System
HRV systems offer significant benefits in regions with harsh climates, providing consistent indoor comfort by recovering heat that would otherwise be lost. They are instrumental in areas where air quality is compromised, ensuring a steady supply of fresh, filtered air. Traditional HVAC systems, with their ability to manage heating and cooling, are adaptable to various climates, from hot summers to cold winters. Their versatility makes them a dependable choice for many homeowners. The choice between an HRV Ventilation System and a traditional HVAC system often hinges on the specific climatic conditions of your area and your household’s particular needs.
Air Quality Advantages
One notable advantage of HRV systems is their continuous air exchange cycle, significantly enhancing indoor air quality by consistently introducing fresh, filtered air. This feature is especially beneficial in urban settings or homes with limited natural ventilation, where outdoor air may contain pollutants. HRV systems also help mitigate humidity and indoor pollutants, creating a healthier living environment.
Traditional HVAC systems can also manage air quality; however, their effectiveness largely depends on the quality of the filters and the frequency of maintenance. Regularly replaced high-efficiency filters can capture airborne particles, including dust, pollen, and other allergens. However, unlike HRV systems, HVAC systems do not provide a constant flow of fresh outdoor air, which can be a limitation in maintaining consistently high air quality.
Space and Visual Appeal
HRV systems offer a more compact solution, concentrating primarily on ventilation needs and allowing for discreet integration within the home. This can be particularly advantageous for properties where space is at a premium, as these systems do not require extensive ductwork. Their design flexibility ensures they blend seamlessly into modern interiors without disrupting aesthetics.
In contrast, traditional HVAC systems often necessitate larger units and a more comprehensive network of ducts, which can occupy significant space and potentially alter the visual layout of your home. The bulkier nature of HVAC components might be a drawback for homeowners who prioritise maintaining a minimalist or streamlined design in their living areas.
Environmental Impact Considerations
HRV systems are engineered to minimise energy waste by recovering heat from outgoing air and using it to warm incoming fresh air. This process significantly reduces the energy required to heat your home, lowering your carbon footprint. In contrast, traditional HVAC systems typically consume more power as they cannot recycle heat efficiently. The energy efficiency of HRV systems makes them a more sustainable option, particularly for households aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
Additionally, HRV systems contribute to better indoor air quality by continuously cycling fresh air into the home, which can also lessen the need for energy-intensive air purifiers. While some modern HVAC systems incorporate energy-saving features, they still rely on greater energy consumption and may use refrigerants with a higher environmental impact.
By focusing on heat recovery and energy conservation, HRV systems offer a greener alternative for maintaining indoor comfort. The reduced reliance on non-renewable energy sources and lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with HRV systems make them an attractive choice for eco-conscious homeowners.
Financial Evaluation
When considering the financial aspects, looking beyond the initial costs is essential. While HRV systems may require a higher upfront investment due to specialised installation and equipment, the potential savings on energy bills can be substantial over time. The efficiency of HRV systems in recovering and reusing heat means that they can significantly lower your heating expenses, resulting in financial benefits in the long run. The improved air quality offered by HRV systems can also reduce medical costs related to respiratory issues, adding another layer of savings.
On the other hand, traditional HVAC systems might have a more accessible initial price point and be easier to integrate into existing homes. However, their ongoing energy consumption can lead to higher utility bills, particularly in homes located in extreme climates requiring frequent heating or cooling. Regular maintenance and potential repairs can also add to the overall costs.
When evaluating financial considerations, immediate expenses and long-term savings must be considered. This comprehensive approach will help you determine the most cost-effective solution tailored to your needs and circumstances.
Concluding Thoughts
Deciding between an HRV Heating System and a traditional HVAC system depends on your home’s unique needs, budget, and climate. HRV systems excel in energy efficiency and air quality, offering a sustainable option for modern homes. However, their higher initial cost and specific installation requirements may make them less accessible for some homeowners. On the other hand, traditional HVAC systems are versatile and more easily retrofitted, making them suitable for various climates and home setups. You can choose the heating system that best aligns with your lifestyle and long-term goals by carefully considering factors like energy efficiency, maintenance, and environmental impact.
FAQs about HRV and HVAC Systems
1. What are the key differences between HRV Heating System and traditional HVAC systems?
HRV Heating System focuses on heat recovery and ventilation, continuously exchanging indoor air with fresh, filtered outdoor air while maintaining energy efficiency. Traditional HVAC systems provide heating and cooling through a furnace or air conditioner, focusing on temperature control rather than ventilation.
2. Which system is more energy-efficient, HRV or HVAC?
HRV systems are generally more energy-efficient due to their heat recovery process, which reuses energy from outgoing air to warm incoming air. In contrast, traditional HVAC systems require more energy to maintain indoor temperatures, although newer models with advanced features may close the efficiency gap.
3. Are HRV systems suitable for all homes?
HRV systems work best in energy-efficient homes with tight construction or in climates with significant temperature differences. They often require dedicated ductwork, making them ideal for new constructions or extensive renovations.
4. What are the maintenance requirements for HRV Ventilation System?
HRV Ventilation System requires regular cleaning of filters and heat exchangers to ensure optimal performance. Maintenance is typically less complex than HVAC systems, which may involve servicing multiple components like furnaces, air conditioners, and ductwork.
5. Which system is more cost-effective in the long term?
While HRV systems have higher upfront costs, their energy savings and improved air quality can offset these expenses over time. Traditional HVAC systems may be cheaper initially but incur higher long-term operating costs due to greater energy consumption and maintenance needs.
| Related Business Listings |
| Contact Directory |
| Local Business Profiles |