Introduction
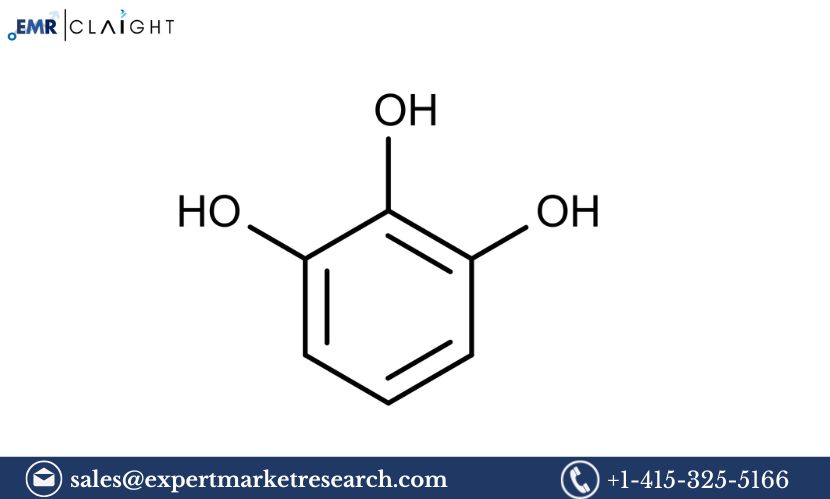
Pyrogallol is a trihydroxy benzene derivative, which makes it a valuable chemical in various industrial applications. It is most commonly produced through the pyrolysis of gallic acid or through the hydroxylation of phenol. Pyrogallol’s primary industrial uses include its role as a developing agent in photographic film, as an antioxidant in cosmetics and food products, and as a chemical intermediate for the production of various dyes and other organic compounds. The Pyrogallol Manufacturing Plant Project Report delves into the technical, financial, and operational aspects of establishing a plant to produce pyrogallol, offering guidance on everything from plant design and required machinery to the potential markets and regulatory requirements.
Key Considerations for Setting Up the Plant
1. Raw Materials and Sourcing
The production of pyrogallol primarily requires the following raw materials:
- Gallic Acid: The most common precursor to pyrogallol, obtained from plant sources such as gallnuts or from synthetic processes. Gallic acid is subjected to pyrolysis (heating in the absence of oxygen) to produce pyrogallol.
- Phenol: An alternative method to produce pyrogallol involves hydroxylating phenol using specific reagents to add hydroxyl groups at the correct positions.
- Catalysts and Reagents: To facilitate the chemical reactions in the manufacturing process, specific catalysts and reagents (such as oxidizing agents) are required.
Sourcing these raw materials is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process. Ensuring a steady and reliable supply chain is essential for maintaining production schedules and meeting market demand.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
2. Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of pyrogallol involves two primary methods: pyrolysis of gallic acid and hydroxylation of phenol. The detailed steps involved in pyrogallol production are as follows:
- Pyrolysis of Gallic Acid: In this method, gallic acid is heated in the absence of air at high temperatures. This process breaks down the gallic acid molecules, leading to the formation of pyrogallol. The reaction also yields by-products such as carbon dioxide and other organic compounds. The process must be carefully controlled to ensure the right temperature and reaction time for optimal pyrogallol yield.
- Hydroxylation of Phenol: In this method, phenol is treated with specific oxidizing agents and catalysts under controlled conditions to introduce hydroxyl groups at the correct positions, resulting in pyrogallol. This method may require less stringent conditions compared to pyrolysis but may involve different reagents and catalysts.
Both methods require precise temperature control, quality monitoring, and a well-maintained production facility to ensure high-quality pyrogallol.
3. Required Equipment and Machinery
To efficiently produce pyrogallol, the manufacturing plant requires specialized equipment and machinery. The primary machinery includes:
- Reactor Vessels: For both pyrolysis and hydroxylation processes, large reactors are required to heat gallic acid or phenol under controlled conditions. These reactors must be designed to withstand high temperatures and pressure, depending on the method used.
- Heating Systems: Since both processes require heating to high temperatures, industrial-grade furnaces or electric heating systems are necessary to maintain the desired reaction conditions.
- Distillation Units: After the reaction, distillation units are used to separate pyrogallol from the reaction mixture. This process ensures that impurities and by-products are removed, leaving behind high-purity pyrogallol.
- Cooling Systems: To control the reaction and ensure safety, effective cooling systems are required to bring the temperature down after the reaction has been completed.
- Purification Equipment: To achieve the desired purity of pyrogallol, filtration and purification systems such as crystallizers and centrifuges may be necessary.
- Packaging Machines: Once the pyrogallol is produced and purified, it must be packaged in suitable containers to preserve its quality during storage and transport.
Efficient operation of this equipment is crucial for maintaining consistent product quality and meeting production targets. It is also important to implement regular maintenance schedules to minimize downtime.
4. Plant Layout and Infrastructure
The design and layout of the pyrogallol manufacturing plant should be optimized for efficiency, safety, and compliance with industry standards. Key areas of the plant include:
- Raw Material Storage: A clean and organized area for storing gallic acid, phenol, and other reagents.
- Production Area: This includes the reactors, distillation units, and purification systems where pyrogallol is produced. The production area should be well-ventilated and capable of handling high temperatures and pressures.
- Quality Control Lab: A dedicated area for testing the quality of pyrogallol and other intermediate products. Regular testing for purity, moisture content, and other parameters is necessary to maintain product standards.
- Packaging Area: The final product must be packaged properly to prevent contamination. This area should be clean and free of dust and moisture.
- Waste Treatment Facility: Given the nature of the production process, a waste treatment facility is required to safely handle by-products and waste generated during manufacturing. This may include filtration systems, waste incinerators, and waste disposal protocols to comply with environmental regulations.
The plant should also have facilities for worker safety, including personal protective equipment (PPE), emergency exits, fire suppression systems, and ventilation systems.
5. Market Demand and Opportunities
The demand for pyrogallol is driven by several factors, including its diverse industrial applications. Some of the key markets include:
- Pharmaceuticals: Pyrogallol is used in the production of pharmaceutical intermediates and as an antioxidant in certain medicines.
- Photography: Pyrogallol was historically used as a developing agent in black-and-white photographic film. Although its use in photography has decreased, there is still niche demand from specialized users.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: Pyrogallol is used as a skin care ingredient due to its antioxidant properties. It is also utilized in the formulation of hair dyes.
- Dye and Pigment Production: As a precursor to various dyes and pigments, pyrogallol is in demand in industries like textiles and leather processing.
- Agriculture: Pyrogallol is sometimes used in certain agricultural chemicals, including those related to plant protection.
The growing interest in natural and sustainable products across various sectors, including the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries, has led to a rise in the demand for pyrogallol. Furthermore, the increasing use of antioxidants in food products and the expanding photo-finishing market can offer profitable opportunities for pyrogallol manufacturers.
6. Financial Feasibility and Investment
Establishing a pyrogallol manufacturing plant requires significant upfront capital investment. Some key financial considerations include:
- Initial Capital Investment: Costs for plant construction, purchasing machinery, obtaining licenses, and setting up the infrastructure.
- Raw Material Costs: Ongoing costs for sourcing raw materials such as gallic acid and phenol.
- Operational Costs: Costs for labor, utilities, maintenance, and quality control.
- Revenue Generation: Revenue will primarily be generated through the sale of pyrogallol to industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and textiles.
- Profit Margins: Profitability depends on production efficiency, raw material sourcing, and market demand. Proper pricing strategies and efficient manufacturing processes will improve margins.
Given the increasing demand for pyrogallol in various sectors, the investment in such a manufacturing plant can yield significant returns in the long term.
FAQs
1. What is pyrogallol used for?
Pyrogallol is primarily used in the pharmaceutical, photographic, and cosmetics industries, as well as in the production of dyes and antioxidants.
2. How is pyrogallol produced?
Pyrogallol is produced by pyrolyzing gallic acid or through the hydroxylation of phenol under controlled conditions.
3. What are the key raw materials for pyrogallol production?
The primary raw materials are gallic acid, phenol, and various catalysts or reagents for the hydroxylation or pyrolysis processes.
4. What industries use pyrogallol?
Pyrogallol is used in pharmaceuticals, photography, cosmetics, textile dyeing, and as an antioxidant in food products.
5. What equipment is needed to manufacture pyrogallol?
Essential equipment includes reactors, distillation units, heating systems, cooling systems, and packaging machines.
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au