Introduction
The establishment of a magnesium oxalate manufacturing plant is a strategic endeavor for those looking to delve into the versatile world of chemical production. Magnesium oxalate is an important compound with a range of applications in industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. This article serves as a comprehensive Magnesium Oxalate Manufacturing Plant Project Report, providing insights into the essentials of setting up a magnesium oxalate manufacturing facility, including its significance, production processes, and key considerations. By understanding the various facets of this venture, stakeholders can make informed decisions that pave the way for successful operations.
Overview of Magnesium Oxalate
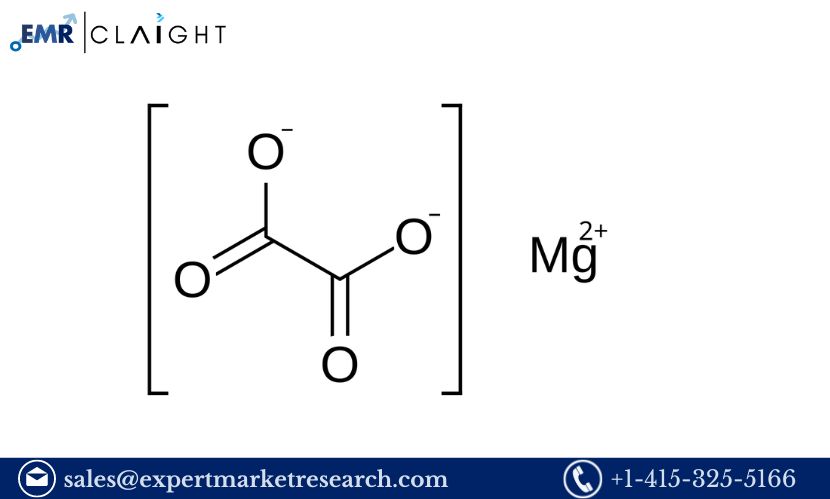
Magnesium oxalate is a white crystalline compound formed from magnesium and oxalic acid. It finds extensive applications in various sectors due to its properties. In agriculture, it is used as a fertilizer and soil amendment, promoting plant growth and improving soil quality. The pharmaceutical industry utilizes magnesium oxalate in the production of specific medications, while food processing industries incorporate it as an additive. Understanding the diverse applications of magnesium oxalate is crucial for manufacturers, as it directly impacts market demand and production strategies.
Definition of Magnesium Oxalate
Magnesium oxalate is defined as a salt formed from the reaction between magnesium ions and oxalic acid. This compound is typically found in two forms: monohydrate and anhydrous, each exhibiting distinct properties and applications. The monohydrate form is particularly useful in the agricultural sector, while the anhydrous variant is often preferred in pharmaceutical formulations. This versatility in application underscores the importance of magnesium oxalate in various industries, highlighting the need for its efficient production.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents @
Manufacturing Process of Magnesium Oxalate
Establishing a manufacturing plant for magnesium oxalate involves several crucial steps. Understanding these processes ensures that production is efficient, cost-effective, and meets quality standards.
1. Raw Material Sourcing
The primary raw materials for producing magnesium oxalate are magnesium salts, typically magnesium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide, and oxalic acid. Sourcing high-quality raw materials is essential, as it directly influences the purity and quality of the final product. Suppliers should be carefully vetted to ensure compliance with industry standards.
2. Reaction Process
The manufacturing process begins with the careful mixing of magnesium salts and oxalic acid in a controlled environment. This stage requires precise conditions to ensure a complete reaction, resulting in the formation of magnesium oxalate.
3. Filtration and Crystallization
Once the reaction is complete, the mixture is subjected to filtration to separate the solid magnesium oxalate from any unreacted materials. The separated product is then crystallized, allowing for the formation of pure magnesium oxalate crystals. This step is critical, as it determines the purity and quality of the end product.
4. Drying and Packaging
After crystallization, the magnesium oxalate is carefully dried to remove any residual moisture. This step is essential to prevent degradation of the product during storage and transport. Once dried, the magnesium oxalate is packaged in suitable containers, ensuring protection from moisture and contamination.
5. Quality Control
Implementing a robust quality control system throughout the manufacturing process is vital. This includes regular testing of raw materials, in-process materials, and the final product to ensure adherence to industry standards. Quality control measures not only guarantee product safety and efficacy but also enhance the overall reputation of the manufacturing plant.
Production Cost Report
When embarking on a magnesium oxalate manufacturing project, understanding the production costs is essential for financial planning. Costs can be categorized into several key areas:
1. Raw Material Costs
The cost of raw materials constitutes a significant portion of the overall production expenses. Securing reliable suppliers can help mitigate fluctuations in prices and ensure a steady supply of quality materials.
2. Equipment and Infrastructure
Investing in high-quality equipment is crucial for efficient production. This includes reactors, filtration systems, drying units, and packaging machines. Additionally, the infrastructure required for the plant, including utilities and waste management systems, should also be considered in the budget.
3. Labor Costs
Skilled labor is essential for the successful operation of a manufacturing plant. This includes technicians, quality control personnel, and administrative staff. Proper training and development programs can enhance workforce efficiency and productivity.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring compliance with local and international regulations is vital for the operation of a magnesium oxalate manufacturing plant. This may involve costs related to permits, licenses, and environmental assessments. Engaging with legal and compliance experts can help navigate these requirements efficiently.
5. Marketing and Distribution
Developing a marketing strategy to promote the magnesium oxalate products is crucial for capturing market share. This includes branding, advertising, and establishing distribution channels. Understanding the target market and competition is essential for effective positioning.
Market Potential and Demand Analysis
The market for magnesium oxalate is influenced by various factors, including industrial demand, agricultural trends, and advancements in pharmaceuticals. The growing emphasis on sustainable agricultural practices drives the demand for fertilizers and soil amendments, positioning magnesium oxalate as a favorable option for farmers. Additionally, the pharmaceutical sector’s need for high-quality excipients enhances the market potential for magnesium oxalate manufacturers.
1. Industry Trends
Monitoring industry trends is vital for staying ahead in the magnesium oxalate market. This includes understanding consumer preferences, technological advancements, and environmental regulations. Manufacturers who adapt to these trends are better positioned to capture market opportunities.
2. Competitive Landscape
Analyzing the competitive landscape allows manufacturers to identify key players and potential collaborators. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of competitors can inform strategic decisions, such as pricing and marketing strategies.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the magnesium oxalate manufacturing sector presents numerous opportunities, it also faces challenges that require careful consideration.
1. Environmental Regulations
Increasingly stringent environmental regulations pose challenges for manufacturers. Adopting eco-friendly production methods and waste management practices can mitigate compliance risks and enhance sustainability.
2. Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chain disruptions can impact the availability of raw materials, leading to production delays and increased costs. Diversifying suppliers and establishing local sourcing strategies can help alleviate these risks.
3. Innovation and R&D
Investing in research and development can lead to the discovery of new applications and formulations for magnesium oxalate, enhancing its market appeal. Continuous innovation can provide a competitive edge in a dynamic market.
FAQ
What is magnesium oxalate used for?
Magnesium oxalate is used in several industries, including agriculture as a fertilizer, in pharmaceuticals as an excipient, and in food processing as an additive. Its versatility makes it a valuable compound in multiple applications.
How is magnesium oxalate produced?
Magnesium oxalate is produced through the reaction of magnesium salts with oxalic acid, followed by processes of filtration, crystallization, drying, and packaging.
What are the main challenges in magnesium oxalate manufacturing?
Challenges include complying with environmental regulations, managing supply chain disruptions, and keeping up with market trends. Addressing these challenges is essential for maintaining efficient operations.
What are the benefits of establishing a magnesium oxalate manufacturing plant?
The benefits include tapping into a growing market demand, diversifying product offerings, and potentially achieving high profitability through efficient production practices.
How can I ensure quality in magnesium oxalate production?
Implementing a robust quality control system that includes regular testing of raw materials and the final product, along with adhering to industry standards, can ensure high-quality production.
Related Reports
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/biometrics-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/portable-generator-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/reports/refrigerator-market/market-size
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au