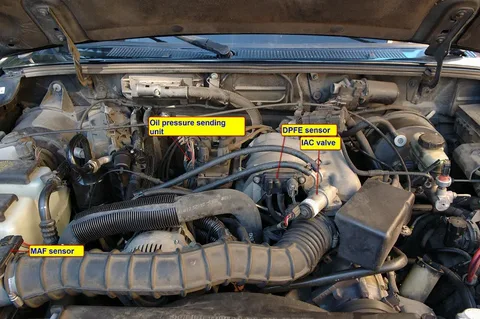
The Ford Ranger is a versatile and popular truck known for its durability and reliability. One of the crucial components that help it achieve optimal performance is the Ford Ranger Map Sensor. This small yet significant device plays a vital role in monitoring the engine’s air intake, directly affecting fuel efficiency and overall engine performance. This blog post will dive deep into the Ford Map Sensor, exploring its function, failure symptoms, maintenance tips, and much more. Understanding how the MAP sensor operates is essential for diagnosing engine issues and ensuring your Ranger runs smoothly.
Understanding the Function of the MAP Sensor in Ford Rangers
The MAP sensor, short for Manifold Absolute Pressure sensor, plays an integral role in the Ford Ranger’s engine management system. This sensor measures the pressure inside the intake manifold, a crucial part of the air intake system. The data collected by the MAP sensor is transmitted to the engine control unit (ECU), which uses this information to calculate the optimal air-fuel mixture for combustion.
The ECU relies on the MAP sensor’s readings to adjust real-time fuel delivery, ignition timing, and other engine parameters. For example, during acceleration, the MAP sensor detects changes in manifold pressure and prompts the ECU to enrich the air-fuel mixture to provide more power. Conversely, the sensor helps the ECU maintain a leaner mixture during steady cruising for better fuel economy.
Furthermore, the MAP sensor aids in engine diagnostics. Abnormal readings can trigger error codes that help identify issues such as vacuum leaks, clogged air filters, or faulty fuel injectors. The sensor’s role in emissions control is also significant; accurate pressure readings help maintain combustion efficiency, reducing harmful emissions.
By continuously monitoring manifold pressure, the MAP sensor ensures that the engine operates efficiently under various driving conditions, from rapid acceleration to smooth idling. This real-time data adjustment is crucial for achieving optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, making the MAP sensor an indispensable component of the Ford Ranger’s engine management system.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty Ford Ranger Map Sensor Issues
A malfunctioning Ford MAP sensor can lead to various performance problems, making it essential to recognise the signs early on. One of the most noticeable symptoms is poor fuel economy. When the MAP sensor fails, the engine control unit (ECU) may receive incorrect pressure readings, leading to an improper air-fuel mixture. This can cause the engine to consume more fuel than necessary, resulting in frequent trips to the gas station.
Another common symptom is a rough idle. If the MAP sensor provides inaccurate data, the ECU might struggle to maintain a stable idle, causing the engine to sputter or vibrate excessively when the vehicle is stationary. This can also lead to stalling, especially when coming to a stop. Decreased engine power is another telltale sign of Ford Ranger MAP sensor issues. The sensor’s role in optimising the air-fuel mixture means that any malfunction can result in a loss of power, making acceleration sluggish and overall performance lacklustre.
This is particularly noticeable when you need extra power, such as during uphill drives or when towing. The check engine light is another indicator. Modern vehicles are equipped with diagnostic systems that illuminate the check engine light when a sensor, like the MAP sensor, sends abnormal readings. If this light comes on, using an OBD-II scanner is crucial to check for specific error codes related to the MAP sensor.
Additionally, you might experience poor throttle response. A faulty MAP sensor can delay the ECU’s adjustments to the air-fuel mixture, leading to a lag between pressing the accelerator and the engine’s response. Increased emissions are also a concern, as an improper air-fuel mixture can result in incomplete combustion, releasing more pollutants into the atmosphere.
How to Diagnose Barina Camshaft Sensor Issues?
Diagnosing camshaft sensor issues involves a systematic approach to pinpoint the root cause of the problem. First, you should use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve stored error codes from the vehicle’s ECU. Common error codes for camshaft sensor issues include P0340 and P0341, which indicate a malfunction in the camshaft position sensor circuit.
Once you have identified the error code, visually inspect the Barina Camshaft Sensor and its surrounding components. Look for signs of physical damage, such as cracks, wear, or oil contamination on the sensor. Additionally, check the wiring harness and connectors for any signs of fraying, corrosion, or loose connections that could affect the sensor’s performance.
Next, test the camshaft sensor’s electrical output using a multimeter. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for the correct specifications and procedures. You’ll need to measure the sensor’s resistance and voltage output to ensure it is within the manufacturer’s specified range. If the readings are outside the acceptable range, the sensor may be faulty and require replacement.
You can also perform a waveform test using an oscilloscope to capture the sensor’s signal pattern. A healthy camshaft sensor will produce a consistent waveform, while a faulty one may show irregularities or interruptions in the signal.
Additionally, consider inspecting the camshaft and related mechanical components for any signs of wear or misalignment that could affect the sensor’s readings. Sometimes, timing belt or chain issues can also lead to camshaft sensor errors.
By following these diagnostic steps, you can accurately identify and address camshaft sensor issues, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly.
Benefits of Regular MAP Sensor Maintenance for Ford Rangers
Regular upkeep of your Ford MAP Sensor offers numerous advantages. Firstly, maintaining a clean and fully operational MAP sensor ensures the engine receives the correct air-fuel mixture, improving fuel efficiency. This helps you save on fuel costs over time. Secondly, an optimally functioning MAP sensor contributes to enhanced engine performance. You’ll notice better throttle response, smoother acceleration, and more reliable power delivery, making your driving experience more enjoyable and efficient.
Another benefit is reduced emissions. A properly working MAP sensor helps the engine run more cleanly, lowering harmful pollutants released into the environment. This not only makes your Ranger more eco-friendly but also helps in passing emissions tests more easily.
Additionally, regular maintenance can prevent unexpected breakdowns. Keeping the MAP sensor in good condition reduces the likelihood of engine performance issues that could lead to costly repairs. This proactive approach can save you significant amounts in repair bills and downtime.
Incorporating MAP sensor checks into your regular vehicle maintenance routine also helps extend the overall lifespan of your engine. Consistent performance and reduced strain on engine components mean fewer major repairs and a longer operational life for your vehicle. Lastly, well-maintained sensors can contribute to a smoother and more stable idle, reducing the chances of stalling and ensuring a more reliable driving experience.
Expert Tips for Extending the Life of Your Astra Camshaft Sensor
Regular maintenance and mindful driving habits can significantly extend the life of your camshaft sensor. Here are some expert tips to help you get the most out of this essential component:
Regular Inspections:
Periodically inspect the camshaft sensor and its wiring harness for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Early detection of issues can prevent sensor failure.
Cleanliness:
Keep the area around the Astra Camshaft Sensor clean. Dirt, oil, and grime can affect the sensor’s performance. If needed, use appropriate cleaning solutions and tools to gently clean the sensor.
Secure Connections:
Ensure that all electrical connectors are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or corroded connections can lead to intermittent sensor issues and inaccurate readings.
Quality Replacement Parts:
Always use high-quality OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts if you need to replace the camshaft sensor. Inferior aftermarket sensors may not provide accurate readings and could fail prematurely.
Mind the Engine Oil:
Check and change your engine oil regularly according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Clean oil helps maintain the overall health of engine components, including the camshaft sensor.
Avoid Extreme Conditions:
Avoid extreme driving conditions such as excessive idling, frequent short trips, or heavy towing, as these can place additional strain on the sensor and other engine components.
Stay on Top of Engine Health:
Address engine issues promptly, such as rough idling, misfires, or poor fuel economy. These symptoms could indicate underlying problems that might affect the camshaft sensor.
Troubleshooting MAP Sensor Error Codes in Ford Rangers
When your Ford Ranger’s check engine light comes on due to a MAP sensor error code, follow these steps to troubleshoot the issue:
Retrieve the Error Code:
Use an OBD-II scanner to identify the specific error code. Common MAP sensor codes include P0106, P0107, and P0108, which point to various pressure sensor circuit issues.
Consult Repair Manuals:
Please refer to your Ford Ranger’s repair manual for detailed information on the error code and recommended troubleshooting steps. This will provide specific guidance tailored to your vehicle model.
Inspect the Sensor:
Perform a visual inspection of the MAP sensor for any visible damage, wear, or contamination. Be sure to check the sensor’s immediate surroundings for any signs of issues affecting its operation.
Check Wiring and Connections:
Ensure all wiring and electrical connections to the MAP sensor are secure and corrosion-free. Loose or damaged connections can lead to inaccurate sensor readings and trigger error codes.
Test Sensor Output:
Use a multimeter to check the sensor’s electrical output against the manufacturer’s specifications. This involves measuring the sensor’s voltage and resistance to confirm it functions correctly.
Clean or Replace the Sensor:
If the sensor is dirty, cleaning it may resolve the issue. However, replacement is necessary if the sensor is faulty or out of specification. Ensure you clear the error codes from the ECU after replacing the sensor.
Conclusion
Regular attention to your Ford Ranger MAP Sensor ensures your engine consistently receives the correct air-fuel mixture, enhancing performance and fuel efficiency. Addressing symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor early on can prevent more severe issues like poor throttle response, increased emissions, and unexpected breakdowns. Proper maintenance saves on costly repairs and contributes to a more enjoyable driving experience and a longer lifespan for your vehicle. By incorporating MAP sensor checks into your routine vehicle maintenance, you’re investing in the overall health and reliability of your Ford Ranger.
FAQS
Q: What is the primary function of the MAP sensor in a Ford Ranger?
A: The primary function of the MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor is to measure the pressure inside the intake manifold and relay this information to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU then uses this data to adjust the air-fuel mixture, ignition timing, and other engine parameters for optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
Q: What are some common symptoms of faulty Ford Ranger MAP sensor?
A: Common symptoms of a faulty Ford Ranger MAP sensor include poor fuel economy, rough idle, stalling, decreased engine power, check engine light illumination, poor throttle response, and increased emissions. If you experience any of these symptoms, inspecting and addressing the issue promptly is important.
Q: Can I drive my Ford Ranger with a faulty MAP sensor?
A: While you can drive with a faulty MAP sensor, it’s not advisable. A malfunctioning MAP sensor can lead to poor fuel economy, reduced engine performance, and increased emissions. Ignoring the issue could also result in more severe engine problems over time.
Q: How can I diagnose issues with my Ford Ranger’s MAP sensor?
A: Diagnosing MAP sensor issues involves retrieving error codes using an OBD-II scanner, performing a visual inspection for damage or contamination, checking wiring and connections, and testing the sensor’s electrical output with a multimeter. If the sensor is dirty, cleaning it may help, but if it’s faulty, replacement is necessary.