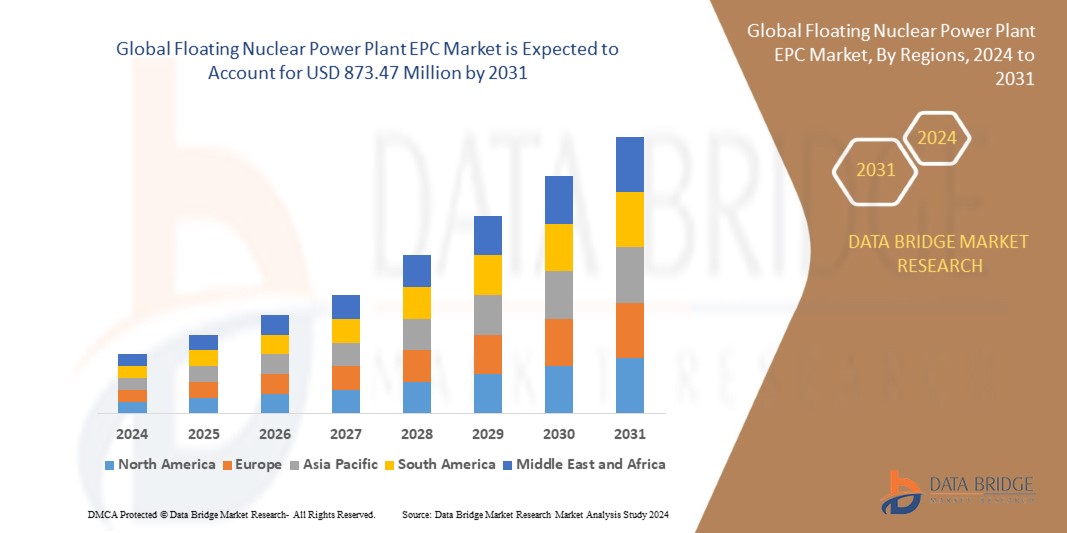
Introduction
The global Floating Nuclear Power Plant (FNPP) EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) Market is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by the increasing demand for clean, stable, and uninterrupted power supply in remote regions and offshore locations. Floating nuclear power plants represent a novel solution to energy needs in isolated coastal and island communities, mining operations, oil and gas platforms, and military bases. As governments and private sectors pursue sustainable and decentralized energy options, the FNPP EPC market is witnessing growing traction.
This article explores the current trends, drivers, challenges, and competitive landscape of the Floating Nuclear Power Plant EPC market, offering insights into its projected growth trajectory up to 2032.
Market Overview
Floating nuclear power plants are ship-like platforms equipped with compact nuclear reactors, often based on pressurized water reactor (PWR) technology. These plants are constructed in shipyards and then towed to the desired offshore or coastal site. Unlike conventional nuclear power plants, FNPPs offer mobility, lower land-use requirements, and the ability to serve remote or resource-scarce regions.
The EPC segment of this market encompasses the design, procurement of materials and equipment, and the actual construction and commissioning of these plants. This full-cycle service makes EPC providers critical stakeholders in the FNPP ecosystem.
In 2024, the global FNPP EPC market is estimated to be valued at over USD 1.8 billion, and it is projected to reach more than USD 5.6 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 15.4% during the forecast period.
Key Market Drivers
1. Energy Demand in Remote Areas
Many island nations and isolated regions rely heavily on diesel generators for electricity, which are costly and environmentally harmful. FNPPs offer a stable and clean energy alternative, significantly reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
2. Decarbonization and Clean Energy Goals
With global climate goals set under the Paris Agreement, countries are exploring various low-carbon technologies. Nuclear energy, including FNPPs, is being re-evaluated for its role in achieving net-zero emissions, especially due to its zero greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
3. Defense and Strategic Infrastructure
Military bases and maritime defense operations often require energy independence. FNPPs can serve as reliable, secure power sources for naval bases, radar stations, and remote military outposts.
4. Technological Advancements in Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
Floating nuclear plants typically employ SMRs, which are safer, more flexible, and economically viable for small-scale applications. SMRs are easier to fabricate and transport, making them well-suited for floating installations.
Challenges Facing the Market
1. Regulatory and Safety Concerns
The deployment of nuclear technology, particularly in floating platforms, poses unique safety and environmental challenges. Regulatory frameworks are still evolving, and international consensus on licensing, decommissioning, and waste management is lacking.
2. High Initial Capital Investment
Despite the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits, FNPPs require substantial initial investment in engineering, design, and construction. This often limits adoption to government-funded or large-scale industrial projects.
3. Public Perception and Opposition
Public skepticism toward nuclear energy remains a significant barrier. Concerns related to nuclear accidents, radioactive waste, and potential misuse hamper the wider acceptance of floating nuclear solutions.
4. Geopolitical Risks
The export and deployment of floating nuclear plants involve cross-border collaboration, which may be impacted by political tensions, sanctions, or trade barriers, especially involving major players like Russia, China, and the U.S.
Market Segmentation
By Reactor Type
-
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
-
Micro Reactors
By Application
-
Remote Community Power Supply
-
Offshore Oil & Gas Platforms
-
Military and Defense
-
Disaster Relief and Emergency Power
By Component
-
Nuclear Reactor
-
Steam Turbine
-
Heat Exchangers
-
Control Systems
-
Electrical Generators
-
Platform and Hull Infrastructure
By Region
-
North America: U.S. and Canada showing early-stage interest with SMR initiatives.
-
Europe: Countries like France and the UK exploring feasibility studies.
-
Asia-Pacific: Russia’s Akademik Lomonosov (the world’s first FNPP), along with China and South Korea, are driving innovation and deployments.
-
Middle East & Africa: Potential demand for desalination and energy in arid coastal zones.
-
Latin America: Brazil and Argentina exploring nuclear for remote regions and mining sites.
Competitive Landscape
The FNPP EPC market is in its nascent but highly competitive phase, with a mix of state-backed agencies, nuclear technology providers, and marine engineering firms. Some key players include:
-
Rosatom (Russia) – Pioneers of the FNPP concept, having deployed the Akademik Lomonosov.
-
NuScale Power (U.S.) – Leading the SMR development in North America.
-
BWX Technologies – Specializing in modular nuclear components and naval reactors.
-
China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC) – Developing floating and land-based SMRs.
-
KEPCO (South Korea) – Engaged in reactor design and export strategies.
Partnerships between shipbuilders, nuclear technology firms, and EPC contractors are becoming increasingly common to streamline design and reduce lead times.
Strategic Developments
-
Government Incentives: Several governments are launching pilot programs and R&D funds to support SMR and FNPP projects.
-
Public-Private Collaborations: Projects increasingly involve collaborations between national energy agencies and private-sector innovators.
-
Technological Innovation: Emphasis on passive safety systems, improved fuel cycles, and hybrid energy integration (e.g., combining nuclear with renewable storage systems).
-
Export Opportunities: Countries with nuclear expertise are looking to export floating nuclear power plants to energy-starved or disaster-prone regions.
Future Outlook
The global Floating Nuclear Power Plant EPC market is poised for significant growth over the next decade, spurred by increasing demand for resilient, clean, and flexible power infrastructure. While the market faces technical and regulatory challenges, the pace of innovation and strategic investment is expected to overcome these barriers.
Countries and organizations that invest early in FNPP technology and supportive EPC infrastructure are likely to gain a competitive edge in both energy security and economic sustainability. Moreover, FNPPs could play a vital role in addressing future energy crises, climate-related disruptions, and the need for energy equity in underdeveloped regions.
Get More Details:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-floating-nuclear-power-plant-epc-market
Conclusion
Floating Nuclear Power Plants represent a promising frontier in the global energy landscape, offering sustainable power generation options in a mobile and modular format. The EPC market is critical to bringing these advanced systems to life, from conceptual design to operational readiness.
With the convergence of nuclear innovation, climate urgency, and decentralized energy needs, the FNPP EPC market is expected to become a cornerstone of next-generation energy solutions. Stakeholders—including governments, private developers, and engineering firms—must now collaborate to shape a safe, efficient, and economically viable future for this emerging sector.