If your business needs precision, speed, and repeatability, then investing in a CNC turning machine might be your smartest move yet. These machines are the backbone of modern manufacturing, shaping everything from aerospace parts to simple metal rods with astonishing accuracy.
In this post, you’ll discover how CNC turning machines work, their key advantages, industry applications, and how they compare to other machining tools. Whether you’re new to CNC or expanding your shop floor, this guide will steer you in the right direction.
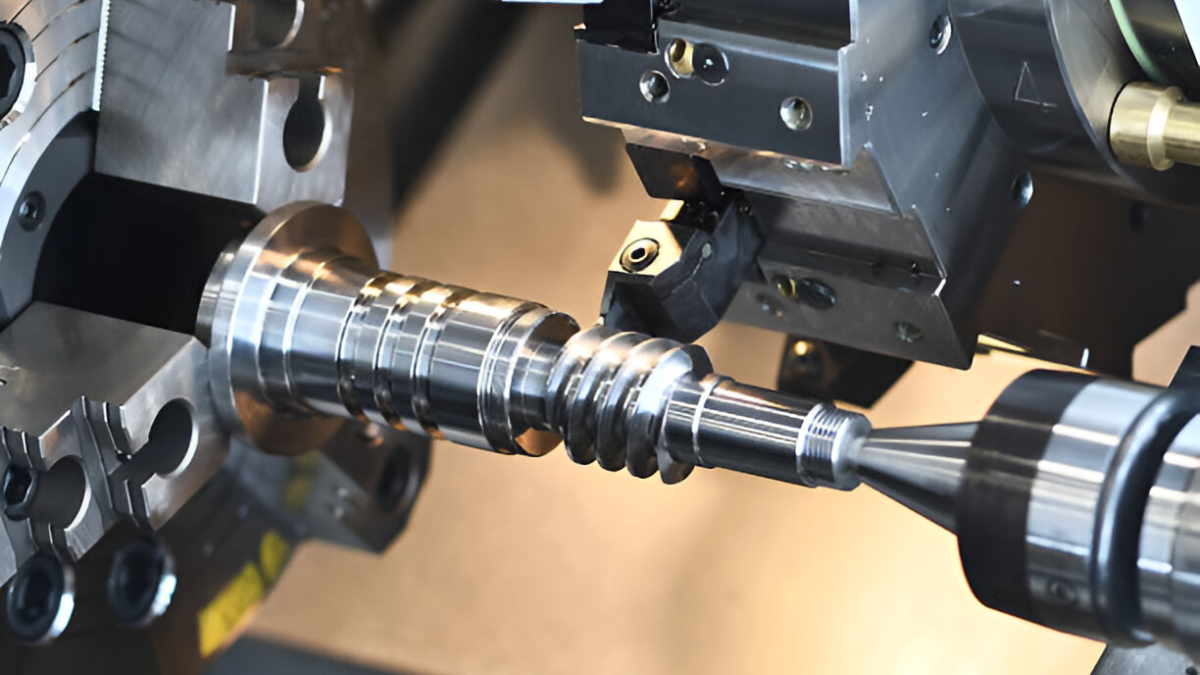
What Is a CNC Turning Machine?
A CNC turning machine is a computer-controlled lathe that rotates a workpiece while a cutting tool removes material, producing a precise cylindrical shape. It’s a core part of subtractive manufacturing, where parts are made by removing layers of material rather than adding them.
The process is automated using G-code, enabling the machine to cut, drill, bore, and face without human intervention. This leads to consistent quality, high productivity, and tight tolerances, even on complex geometries.
Core Components of a CNC Turning Machine
To better understand how this powerhouse works, let’s break down its main components:
- Chuck: Grips and rotates the workpiece.
- Spindle: Drives the chuck’s rotation.
- Tool turret: Holds multiple cutting tools and switches between them as needed.
- Controller: Interprets the program (G-code) and translates it into motion.
- Bed: Supports the entire structure for stability and accuracy.
Combined, these parts deliver the performance manufacturers rely on for mass production and prototyping.
CNC Turning Machine vs. CNC Milling Machine
While both are crucial in CNC machining, they serve different roles.
| Feature | CNC Turning Machine | CNC Milling Machine |
| Movement | Workpiece rotates | Tool rotates |
| Best for | Cylindrical parts | Complex, prismatic parts |
| Material removal | Along linear axes | In multiple directions |
| Production speed | Faster for round items | Slower but more flexible |
So, when you’re dealing with shafts, pins, bushings, or rods, a CNC turning machine is the clear winner.
12 Advantages of Using a CNC Turning Machine
1. Precision Turning
These machines achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 mm, ideal for high-accuracy projects.
2. High-Speed Production
Rotational speeds can exceed 6,000 RPM, accelerating mass production without sacrificing quality.
3. CNC Turning Services Save Costs
Outsourcing to a provider offering CNC turning services eliminates the need for costly equipment and training.
4. Lower Labor Dependency
Once programmed, machines run automatically with minimal operator input.
5. Scalability
From prototyping to full-scale manufacturing, CNC turning can easily adjust production volumes.
6. Reduced Material Waste
The precision of CNC turning reduces excess cuts, saving raw material and cutting costs.
7. Versatility
Compatible with metals, plastics, and composites—ideal for diverse industries.
8. Repeatability
Thousands of identical parts can be made with no variation in quality.
9. Fewer Errors
Advanced software controls reduce the margin of human error dramatically.
10. Easy to Automate
Modern machines integrate with bar feeders and robotic arms for 24/7 operation.
11. Enhanced Safety
Operators are not in direct contact with the cutting area, reducing injury risks.
12. Compact Footprint
Even industrial-grade turning machines have a smaller footprint than other heavy-duty machines.
Common Materials Used in CNC Turning
CNC turning machines handle a wide variety of materials, including:
- Metals: Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, brass, and copper
- Plastics: Nylon, ABS, PEEK, and polycarbonate
- Composites: Fiber-reinforced polymers used in automotive and aerospace
The ability to work with these materials makes CNC turning a top choice for industries requiring precision turning and custom CNC parts.
Industrial Applications of CNC Turning Machines
These machines are used across sectors where detail, strength, and accuracy matter most.
| Industry | Common Products Made |
| Aerospace | Turbine shafts, fasteners |
| Automotive | Gear blanks, pistons, drive shafts |
| Medical | Implants, surgical screws |
| Electronics | Connector pins, casings |
| Oil & Gas | Pipe fittings, pressure valve parts |
Because they deliver reliable performance, CNC turning machines are an essential part of industrial CNC equipment setups worldwide.
What to Look for in a CNC Turning Machine
When evaluating machines for your shop or outsourcing partner, consider these critical specs:
Spindle Speed and Power
Higher speeds mean smoother finishes and quicker cycles.
Tool Turret Capacity
The more tools it holds, the more operations you can perform without stopping.
Machining Envelope
Ensure it fits the maximum dimensions of the parts you plan to produce.
Controller Type
Modern controls like FANUC or Siemens simplify programming and troubleshooting.
Automation Features
Look for bar feeders, robotic arms, and coolant systems that support automated turning machine setups.
CNC Lathe Operations: What Can You Do?
A CNC lathe machine isn’t just for basic shaping. With the right tooling and programming, it can perform:
- Facing: Creating a flat surface at the end of the part
- Turning: Reducing the diameter along the part’s length
- Grooving: Cutting slots or recesses
- Threading: Making internal or external threads
- Drilling: Boring holes into the rotating workpiece
These CNC lathe operations increase the value and complexity of parts made on a turning machine.
CNC Machining Center vs. Turning Machine: Which Is Better?
A CNC machining center often combines milling, drilling, and tapping in one setup, while a turning machine focuses on rotational symmetry. If your project involves round parts, go with turning. For boxy or 3D-contoured components, opt for a machining center—or use both for hybrid setups.
Maintaining a CNC Turning Machine: Best Practices
Daily Tasks
- Clean chips and debris from the machine bed
- Check tool wear
- Inspect the coolant level and concentration
Weekly Tasks
- Lubricate all moving parts
- Verify spindle and chuck alignment
- Update the control software if needed
Monthly Tasks
- Calibrate tools and sensors
- Clean filters and vents
- Inspect safety features
Regular maintenance ensures longevity, accuracy, and safety in your metal turning machine operations.
The Future of CNC Turning Machines
As manufacturing evolves, so does CNC technology. Many modern turning machines feature:
- AI-driven optimization for real-time toolpath correction
- IoT sensors for predictive maintenance
- Remote monitoring for performance tracking
These smart innovations turn traditional machines into intelligent systems, setting the standard for future-ready CNC parts production.
Final Thoughts
A CNC turning machine is a precision tool that transforms raw material into finely crafted components at scale. Whether you’re looking to optimize your in-house production or partner with a service provider, understanding the value of CNC turning is key.
From custom prototypes to high-volume production, this technology continues to shape industries worldwide with efficiency, reliability, and unmatched accuracy.